Introduction
Intellectual property forms the backbone of many successful businesses by protecting unique creations, inventions, and brand identities from unauthorized use. For business owners, understanding the wide range of intellectual property (IP) examples is crucial to safeguarding what makes your company distinctive and competitive. From creative works secured by copyrights to inventive designs covered by patents, and from memorable brand identifiers to confidential trade secrets, each type of IP serves a specific purpose. This guide explores the most common IP categories and demonstrates how they intersect with business products and services. By delving into copyrights, trademarks, patents, trade secrets, industrial designs, service marks, and combined protections, you will gain a comprehensive perspective on how IP can be leveraged to protect and grow your business effectively.
Tables of Contents
Chapter 1: Examples of Intellectual Property: Copyrights in Creative Works
- How Copyrights Secure Creative Expression Through Legal and Technological Protections
- Embracing Creativity Across Mediums: Copyright Protection in Diverse Artistic Expressions
Chapter 2: Examples of Intellectual Property: Trademarks as Brand Identifiers
- Iconic Trademarks Shaping Global Brand Identities Through Distinctive Symbols
- Trademarks as Strategic Brand Identifiers: Building Recognition and Loyalty Through Intellectual Property
Chapter 3: Innovative Patents Driving Technological and Design Breakthroughs
- Harnessing Patent Protection to Propel Technological Innovation and Sustainable Designs
- Navigating the Economic and Geopolitical Landscape of Patents in Innovation and Design
Chapter 4: Trade Secrets as Key Examples of Intellectual Property Protecting Confidential Assets
- Unlocking the Power of Trade Secrets: Vital Confidential Business Information in Intellectual Property
- Safeguarding Innovation: The Role of Trade Secrets and Confidential Business Information in Intellectual Property Protection
Chapter 5: Examples of Intellectual Property: Industrial Designs and Service Marks
- How Industrial Designs Shape Product Identity Through Visual Innovation
- How Service Marks Secure Service Brands and Shape Market Identity
Chapter 6: Examples of Intellectual Property: Combined Intellectual Property Protections in Products
- Layered Legal Safeguards: How Integrated Intellectual Property Protections Secure Innovative Products
- Harnessing Multiple Intellectual Property Rights: Strategic Layers of Protection and Enforcement in Product Innovation
Chapter 1: Examples of Intellectual Property: Copyrights in Creative Works

1. How Copyrights Secure Creative Expression Through Legal and Technological Protections
Copyrights provide creators with a powerful legal framework to protect original works from unauthorized use. Once an original work is fixed in a tangible form—be it a manuscript, digital file, or recorded performance—copyright protection arises automatically. This automatic coverage ensures creators immediately hold exclusive rights to reproduce, distribute, display, perform, and prepare derivative works based on their creation without requiring formal registration.
However, registering a copyright with a governing agency significantly strengthens these protections. It serves as formal evidence of ownership and enables copyright holders to pursue legal enforcement more effectively. Through civil litigation, creators can seek injunctions to halt unauthorized use and claim monetary damages for infringement, thereby upholding the value of their intellectual property.
In modern contexts, copyright protection also extends into the digital realm. Mechanisms like Digital Rights Management (DRM) systems, anti-circumvention laws, and automated content recognition technologies play a critical role in detecting and preventing illegal copying or distribution of digital content online. Creators often supplement these legal tools with technological safeguards such as digital watermarks, encryption, and access controls to further secure their works.
Moreover, copyright holders have flexibility in disposition through licensing. They can grant permissions under specified terms or adopt open licenses—like Creative Commons—that allow certain uses while maintaining core rights. This licensing flexibility reduces disputes and fosters wider dissemination balanced with protection.
The scope of copyright covers a diverse range of creative outputs, including literary texts, music, films, visual arts, architectural designs, and software programs. Protection typically endures for the life of the author plus an extended period, commonly 70 years, offering long-term security and economic incentives.
For business owners interested in deeper insights on copyright mechanics, especially regarding distribution rights and enforceability, see the comprehensive resource on copyright distribution rights.
2. Embracing Creativity Across Mediums: Copyright Protection in Diverse Artistic Expressions
Embracing Creativity Across Mediums: Copyright Protection in Diverse Artistic Expressions
Copyright law extends its protective scope to a wide spectrum of creative endeavors, encompassing literary works, music, visual arts, film, choreography, architecture, software, and digital content. This broad coverage safeguards original works of authorship once they are fixed in a tangible form, giving creators exclusive rights to reproduce, distribute, perform, display, and adapt their creations.
Literary works include novels, poems, plays, and articles, each reflecting unique voices and narratives. Musical works cover both compositions and sound recordings, protecting not only the written score but also the final audio production. Visual arts such as paintings, drawings, photographs, and sculptures find protection that preserves their artistic integrity from unauthorized copying or alteration. Films and audiovisual works combine visual and musical elements, while choreography and performances gain protection when documented through notation or fixation.
Architectural designs are protected through copyrights once blueprints or constructed buildings embody creative expression. Software and digital contents, including websites and databases with creative input, are also encompassed, highlighting modern expansion in copyright’s reach.
These protections arise automatically upon creation and fixation, typically enduring for the creator’s life plus 70 years, empowering creators to control and monetize their work. Licensing frameworks like Creative Commons enable flexible sharing while maintaining essential rights such as attribution.
This extensive protection framework affirms copyrights as a fundamental pillar of intellectual property, ensuring that creators across multiple mediums retain authority over the use and distribution of their original works. For a focused exploration of how copyright functions in business, including definitions and economic aspects, see detailed insights at copyright definition economics business.
Chapter 2: Examples of Intellectual Property: Trademarks as Brand Identifiers

1. Iconic Trademarks Shaping Global Brand Identities Through Distinctive Symbols
Iconic Trademarks Shaping Global Brand Identities Through Distinctive Symbols
Trademarks are powerful intellectual property tools that protect the unique identifiers of global brands, fostering instant recognition and consumer loyalty. These legal protections extend beyond names to include logos, slogans, shapes, sounds, colors, and even gestures that embody a brand’s identity. For example, a simple swoosh has transcended its origins to symbolize speed, quality, and aspiration worldwide, while a memorable slogan can carry powerful emotional resonance across cultures and industries.
Some of the most recognized trademarks include distinctive script logos crafted over a century ago, which still evoke tradition and trust, paired with product designs patented for exclusivity. The visual consistency of such trademarks, along with legal defenses in landmark cases, protects these brands from imitators and consumer confusion. Iconic architectural or logo designs stand as symbols synonymous with quality or luxury, providing a cohesive brand image recognized on every continent.
Trademarks also embrace cultural symbolism, integrating colors and design motifs that honor heritage while appealing to global markets. Beyond visuals, trademarking sounds like a stock exchange bell or signature phrases in entertainment events demonstrate the broad scope of brand elements safeguarded under trademark law. Even unique gestures that become synonymous with a personality or brand can be legally protected, showing trademarks’ reach into nontraditional identifiers.
Through these diverse trademark protections, brands secure their intangible assets, reinforcing their marketplace presence and building lasting value. For businesses seeking to understand how to protect their names, logos, and other brand identifiers, resources like trademark2go.com offer valuable guidance on trademark protection for business names and logos.
2. Trademarks as Strategic Brand Identifiers: Building Recognition and Loyalty Through Intellectual Property
Trademarks serve as powerful intellectual property tools that legally protect symbols, words, phrases, or designs that distinguish one company’s goods or services from those of others. These brand identifiers extend beyond simple logos to embody the entire essence of a brand’s presence in the marketplace. Iconic visual marks instantly evoke qualities such as reliability, uniqueness, or prestige, creating immediate recognition among consumers. The effectiveness of a trademark often depends on its distinctiveness. Brands that adopt arbitrary or unique terms find stronger legal protection and greater memorability compared to those with generic or descriptive marks.
Beyond legal protection, trademarks play a pivotal strategic role in shaping brand identity. They capture the brand’s core values, personality, and promises, conveying this message consistently across all customer touchpoints. Through deliberate use of color schemes, typography, and designs, trademarks reinforce a brand’s narrative and help forge emotional connections with audiences. Consistently applied trademarks serve as familiar signals that nurture consumer loyalty and trust, even when brands expand into unfamiliar markets. This familiarity helps bridge cultural or geographic divides, allowing brands to establish credibility quickly.
Strategically crafted trademarks also aid brands in expanding their influence both geographically and across product categories. They provide a visual and conceptual anchor that supports brand coherence while enabling growth and diversification without diluting the original identity. By protecting these critical elements of brand identity, trademarks ensure businesses maintain competitive advantages and build lasting customer relationships.
For those interested in protecting these vital brand elements effectively, resources outlining trademark protection for business names and logos offer valuable insights into how companies can secure and leverage their intellectual property.
Chapter 3: Innovative Patents Driving Technological and Design Breakthroughs

1. Harnessing Patent Protection to Propel Technological Innovation and Sustainable Designs
Harnessing Patent Protection to Propel Technological Innovation and Sustainable Designs
Patents serve as powerful tools in safeguarding inventions and designs, playing a pivotal role in advancing technology. By granting inventors exclusive rights, patents create incentives for research and development across diverse fields such as artificial intelligence, blockchain, and the Internet of Things. These technologies demand forward-thinking patent strategies that not only protect current inventions but also accommodate evolving improvements and cross-sector integration.
In sustainability, patents have accelerated innovations in green technologies. Early protections for wind turbine blade designs and mechanical systems have evolved into patents for AI-enhanced monitoring and corrosion-resistant materials. Similarly, patented processes in carbon capture improve efficiency and cost-effectiveness, exemplifying how IP rights align environmental goals with technological progress. This intersection highlights the dynamic role patents play in promoting eco-conscious innovation.
The legal framework surrounding patents fosters a competitive environment that fuels continuous technological advancement. For example, protection of electric vehicle components and autonomous driving systems has stimulated substantial investment and rapid evolution in the automotive industry. Though patent disputes and non-practicing entities can complicate this landscape, emerging AI-driven patent analytics assist in navigating these challenges by providing thorough patent landscape insights and defensive strategies.
Design patents complement invention patents by protecting aesthetic innovations that support sustainability. Modular designs facilitating easier repairs and recycling epitomize how patented designs contribute to circular economy models. These protections enable new business approaches that prioritize resource efficiency and environmental stewardship.
Together, patents for inventions and designs are instrumental in shaping the technological future. They underpin investment, safeguard creativity, and encourage sustainable development, ensuring intellectual property remains a cornerstone of innovation. Explore more on how patents empower innovation in the article about categories of intellectual property rights.
2. Navigating the Economic and Geopolitical Landscape of Patents in Innovation and Design
Patents on inventions and designs do more than protect individual creativity—they influence economies and geopolitical relationships on a profound scale. Economically, patents stimulate innovation by granting inventors exclusive rights to market and profit from their creations, encouraging investment in new technologies and products. This exclusivity fosters growth and competitiveness, especially in nations with well-developed patent systems, ensuring inventors can benefit financially without immediate imitation. However, challenges such as patent backlogs and lengthy examination periods can dampen this incentive by introducing uncertainty, particularly impacting startups and rapidly evolving sectors like biotechnology and electronics.
Beyond economic growth, patent enforcement raises critical questions about equitable access to vital innovations. Strict protection can limit availability of life-saving medicines or sustainable technologies in less affluent regions, prompting initiatives that attempt to balance encouraging innovation with broader social needs. This delicate equilibrium requires policies that support innovation while fostering accessibility, especially in developing countries.
Geopolitically, patents serve as instruments of national strategy. Countries use their IP systems to secure leadership in key technology areas, shaping global competitive dynamics. Contrasting approaches reflect broader economic models: some emphasize robust legal frameworks and market incentives, while others rely on state-supported industrial scaling. Export controls and invention secrecy measures further complicate this landscape, restricting technology flows for national security but potentially impeding broader scientific advancement.
Cultural and legal variations also color the international patent framework. Distinct protections reflecting local identity and economic priorities can create complexities in global trade and IP governance. Navigating these intersecting economic and geopolitical factors reveals patents as pivotal elements shaping not only innovation but also the global distribution of technology and power.
For insights into the broader context of intellectual property protections and their role in business, see our detailed discussion of trademark protection for brand names and logos.
Chapter 4: Trade Secrets as Key Examples of Intellectual Property Protecting Confidential Assets

1. Unlocking the Power of Trade Secrets: Vital Confidential Business Information in Intellectual Property
Trade secrets represent a vital form of intellectual property that safeguards valuable, confidential information critical to a business’s success and competitive strength. Unlike patents or trademarks, trade secrets do not require public disclosure or formal registration but rely entirely on keeping the information secret through diligent protection strategies. The scope of trade secrets is broad, encompassing proprietary formulas, unique manufacturing techniques, algorithms, business strategies, and even client or supplier data. Their value lies in exclusivity — these are insights or practices unknown to competitors and often difficult to replicate once revealed.
To qualify as a protected trade secret, the information must not be generally known or easily discoverable. The holder must also implement reasonable efforts to maintain its secrecy such as restricting access through nondisclosure agreements, physical security measures, and robust internal policies. Legal protection is provided by statutes like the Uniform Trade Secrets Act and the Defend Trade Secrets Act, which enable companies to seek remedies in cases of theft or misappropriation.
Classic examples illustrate how trade secrets safeguard business identity and market positioning. Secret recipes drive product uniqueness, proprietary algorithms shape customer engagement, and specialized manufacturing processes can define product quality. These secrets help businesses retain an edge in innovation and service delivery, often underpinning their most valuable assets.
Because trade secret protection hinges on confidentiality and careful stewardship rather than registration, it demands continuous vigilance. This form of intellectual property complements other protections by covering knowledge and practices that patents or copyrights may not encompass, making trade secrets indispensable for comprehensive intellectual property strategies.
For further insights on protecting business intellectual property and the nuances of different protections, explore the detailed resources available at company intellectual property protection.
2. Safeguarding Innovation: The Role of Trade Secrets and Confidential Business Information in Intellectual Property Protection
Confidential business information forms a critical yet often unseen pillar of intellectual property protection. Unlike patents or trademarks, trade secrets consist of knowledge that derives value precisely because it remains undisclosed. These secrets—ranging from formulas and processes to algorithms and unique business strategies—are powerful assets that companies guard meticulously to maintain competitive advantage. For instance, a carefully guarded formula or proprietary method cannot be legally duplicated without authorization, provided it meets the threshold of secrecy, commercial value, and reasonable protective measures.
Beyond trade secrets, confidential information also includes sensitive corporate data such as employee records, financial reports, and client databases. While not always qualifying as trade secrets, this information requires robust safeguards to protect business integrity and comply with legal obligations. Unauthorized disclosure of such data can result in significant reputational harm and legal penalties.
Legal protection of trade secrets primarily relies on contractual agreements like non-disclosure agreements (NDAs), which bind parties to confidentiality. These agreements, combined with internal security policies such as controlled access, encrypted storage, and employee training, create practical barriers against information leaks. U.S. federal statutes, including the Economic Espionage Act and the Defend Trade Secrets Act, further reinforce this protection by criminalizing misappropriation and enabling civil claims.
Internationally, the treatment of trade secrets varies but generally centers on maintaining secrecy, economic value, and protective efforts. For example, some countries define trade secrets to encompass both technical and business information, mandating tailored legal frameworks that reflect local commercial practices.
Understanding the nuanced interplay of legal, contractual, and operational defenses surrounding confidential business information is essential for businesses aiming to secure their intellectual property. This layered approach not only shields vital knowledge but also sustains innovation, competitiveness, and trust in dynamic markets.
For additional insights on trademarks as part of intellectual property, exploring their protection can provide a complementary perspective on safeguarding brand identity.
Chapter 5: Examples of Intellectual Property: Industrial Designs and Service Marks

1. How Industrial Designs Shape Product Identity Through Visual Innovation
Industrial designs serve as a distinct form of intellectual property devoted to protecting the ornamental and aesthetic qualities of products. Unlike patents, which safeguard functional innovations, industrial designs focus exclusively on the visual elements that make products unique and appealing, such as shape, pattern, or surface ornamentation. This protection plays a critical role in industries where product appearance significantly influences consumer choice and brand differentiation.
Products ranging from consumer electronics to fashion items showcase how industrial designs preserve market identity. For instance, the ergonomic contours of a handheld device or the sleek minimalism of a coffee maker’s exterior are covered under this IP category. Even textile patterns and garment shapes fall within industrial design protections, enabling apparel brands to defend their exclusive visual trademarks. The ornamental features of furniture or household lighting fixtures also exemplify the scope of industrial design rights, emphasizing the interplay between aesthetics and commercial appeal.
The legal protection granted is grounded solely in the novel visual look of a product, without regard to its functional or technical attributes. This allows businesses to secure exclusive rights to their product’s distinctive style for a limited term—usually between 10 and 15 years—encouraging creativity and investment in design innovation. By preventing unauthorized copying, industrial designs enhance a company’s competitive edge, helping maintain a strong market presence.
Through this form of intellectual property, companies protect much more than utility; they safeguard the artistic elements that contribute to brand recognition and consumer loyalty. For more insight on protecting brand visuals and design elements, see this comprehensive resource on trademark protection in business logos and identities.
2. How Service Marks Secure Service Brands and Shape Market Identity
Service marks serve as a vital category of intellectual property specifically designed to protect the identity and branding of services rather than tangible products. Unlike trademarks that focus on physical goods, service marks distinguish the source of intangible offerings by safeguarding names, phrases, logos, or symbols associated with specific services. This protection allows businesses and organizations to build and maintain strong reputations in the marketplace, ensuring that consumers recognize and trust the origin of the service they receive.
For instance, service marks can cover a wide range of industries—from digital platforms that provide innovative online methods to public institutions delivering health or security services, all relying on unique identifiers to stand apart. These identifiers become synonymous with customer expectations and experience, making them invaluable assets. Registering service marks with the appropriate authorities grants exclusive rights, empowering businesses to prevent imitation or dilution of their brand by competitors. The use of service mark symbols, such as ℠ before official registration and ® after, signals ownership and deters infringement.
Maintaining these protections requires vigilant monitoring and enforcement to protect market position and consumer confidence. This ongoing stewardship preserves the link between the service and its source, a connection fundamental to marketing, reputation, and customer loyalty. In commercial ecosystems where services often compete on reputation and distinctiveness rather than just product features, service marks are indispensable for safeguarding branding strategies.
Understanding how service marks operate within the broader framework of intellectual property deepens appreciation for their role in differentiating service brands and securing competitive advantage. For a comprehensive look at trademark protections that encompass service marks, refer to detailed resources such as trademark protection for business names and logos.
Chapter 6: Examples of Intellectual Property: Combined Intellectual Property Protections in Products
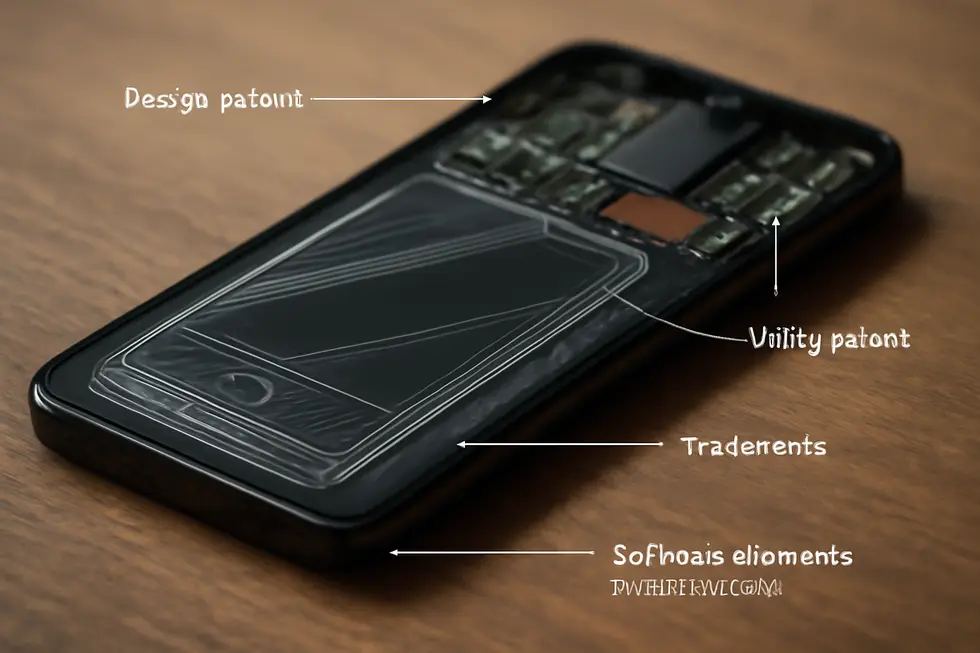
1. Layered Legal Safeguards: How Integrated Intellectual Property Protections Secure Innovative Products
Intellectual property protection often involves a strategic layering of legal rights to fully secure the many dimensions of a product. Inventors and companies typically employ a combination of patents, trademarks, design patents, and trade dress to cover technology, branding, and product design comprehensively. Patents shield the functional and technological innovations, granting exclusive rights to novel processes, machines, or chemicals, which helps prevent direct copying and encourages investment in research and development. Meanwhile, trademarks protect the symbols, names, and slogans that create brand recognition in the marketplace, often registered both separately and combined to maximize enforcement flexibility. Design patents add a critical layer by safeguarding the unique ornamental appearance of products, offering quick and enforceable protection for aesthetic elements that contribute to consumer appeal. Complementing these, trade dress covers the overall look and feel of a product, including packaging and distinctive visual design features established through consumer association over time. Together, these protections form an intricate legal framework that defends multiple facets of a product simultaneously, creating formidable barriers against infringement and unauthorized use.
This multilevel IP approach also aligns with evolving technologies and legal requirements. Companies must adapt their strategies as innovations become more complex and branding extends into digital or auditory realms. For example, emerging technologies require refined patent applications, while trademarks now increasingly encompass nontraditional marks related to AI interfaces and sounds. Legal frameworks set the boundaries for these protections, but business strategies leverage IP portfolios to enhance market positioning, facilitate licensing, and support collaboration. This interconnectedness between technology and law highlights how comprehensive intellectual property protection is essential to maintain competitive advantages and foster ongoing innovation.
For businesses aiming to fully protect their brand identity and product innovations, understanding the value of combined IP protections is vital. More insights on trademark strategies for protecting names and logos can be explored at trademark protection for business names and logos.
2. Harnessing Multiple Intellectual Property Rights: Strategic Layers of Protection and Enforcement in Product Innovation
Effectively safeguarding a product today often requires a strategic blend of intellectual property (IP) protections, weaving together patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets to build a resilient commercial fortress. This layered approach does more than simply guard innovation—it creates a multifaceted shield that deters competitors from encroaching on distinct aspects of a product, whether technological, aesthetic, or brand-related.
Patents secure the backbone of innovation by protecting functional advancements and novel technologies, preventing direct copying of the invention itself. Complementing this, trademarks defend the visual and verbal identity—brand names, logos, and slogans—that assure consumers of quality and origin. Combining trademarks as a single mark or as separate registrations for names and logos allows businesses to tailor protection depth and flexibility depending on their branding strategy.
Copyrights add another dimension by protecting the expressive elements linked to a product, such as software code, user manuals, or marketing materials. Simultaneously, trade secrets guard proprietary processes or formulas that provide competitive advantages without public disclosure, preserving exclusivity indefinitely if confidentiality is maintained.
From an enforcement view, this synergy compels businesses to agilely monitor risks like patent expiration or potential infringements, adapting legal strategies accordingly. Close coordination between legal and product teams fosters innovation while ensuring IP assets align with evolving market challenges. Litigation trends further inform this dynamic, helping companies anticipate threats and optimize defense or licensing tactics.
Ultimately, integrating multiple IP rights creates a comprehensive barrier against imitation. This strategy balances investment with protection scope and supports sustainable market leadership, empowering businesses to protect not just an invention or brand but the entire product ecosystem.
For businesses exploring brand identity protections alongside patents and copyrights, resources about trademark protection for business names and logos offer valuable strategic insights.
Final thoughts
Recognizing the diverse examples of intellectual property equips business owners with the knowledge to protect every valuable aspect of their enterprise effectively. Each IP type—whether it’s the creative brilliance secured by copyrights, the distinctive identity upheld by trademarks, the innovative solutions shielded by patents, or the vital advantages maintained through trade secrets—plays a strategic role in business success. Industrial designs and service marks further widen this protective net, while combined IP protections demonstrate the layered security possible for complex products. Armed with this holistic understanding, you can navigate IP strategies confidently to defend your unique ideas, foster innovation, and sustain competitive advantage in your market.
Your IP is the foundation of your success – let’s protect it together before it’s too late. We can’t wait to help you turn your ideas into legally secured assets.
About us
undefined


